The Power of Plant-Based Diets: A Comprehensive Look at Their Nutritional Benefits
The human diet has seen a multitude of shifts throughout history. From the hunter-gatherer days of the Paleolithic era to the advent of agriculture, our nutritional habits have been shaped by societal and environmental factors. The modern age, with its increased awareness of health and wellness, has witnessed a resurgence of plant-based diets. While vegetarianism and veganism have been part of human society for thousands of years, primarily driven by religious and philosophical beliefs, today's plant-based movement is also fueled by health consciousness, environmental concerns, and animal rights advocacy.

Understanding Plant-Based Diets
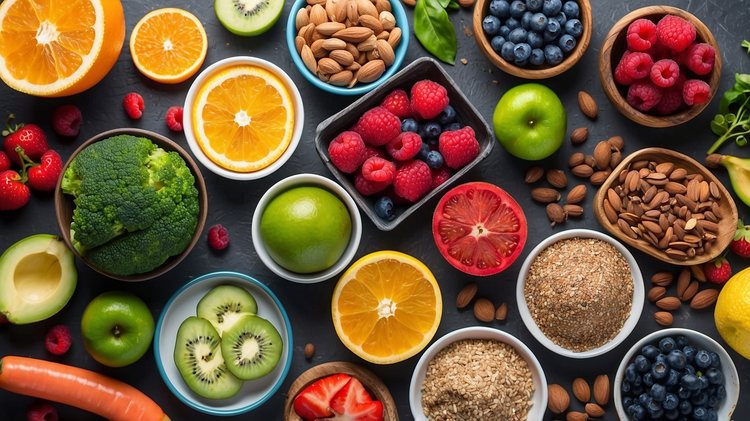
Plant-based diets, in essence, emphasize foods derived from plants. This includes not only fruits and vegetables, but also whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes. There are different degrees of plant-based diets, ranging from vegan diets which completely exclude animal products, to flexitarian diets, where animal products are minimally consumed.
It’s worth noting that a plant-based diet is not automatically a healthy diet. Just as it’s possible to have an unhealthy omnivorous diet, plant-based diets can also be poorly balanced if they rely heavily on processed foods or lack a variety of nutrient sources.
Nutritional Value of Plant-Based Diets
A well-planned plant-based diet can be nutritionally adequate and offer numerous health benefits. Plant foods are packed with a plethora of nutrients including fiber, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. They are also typically low in saturated fat and devoid of cholesterol.
Fiber is a standout feature of plant-based diets. It promotes digestive health, aids in weight management, and has been linked to lower rates of heart disease and certain types of cancer. Antioxidants, found abundantly in fruits and vegetables, help protect the body against the damage caused by free radicals, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
The key to a nutrient-rich plant-based diet is diversity. Consuming a wide range of plant foods ensures a broad spectrum of nutrients. For example, legumes are an excellent source of protein and iron, nuts and seeds provide healthy fats and vitamin E, while whole grains supply B-vitamins and complex carbohydrates.
Managing Diseases with Plant-Based Diets
One of the most impactful benefits of plant-based diets is their potential role in disease prevention and management. A wealth of research suggests that plant-based diets can help in managing diseases like obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer.
High in fiber and low in saturated fat, plant-based diets can aid in weight management and enhance cardiovascular health. They have been shown to lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and reduce the risk of heart disease.
For diabetes management, the high fiber content and low glycemic load of plant-based diets can help regulate blood sugar levels. Moreover, the phytochemicals found in plant foods may help in preventing the onset of cancer by boosting the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
Challenges and Considerations in Adopting a Plant-Based Diet
While plant-based diets have undeniable benefits, they also come with their own set of challenges. Nutritional deficiencies are a concern, particularly for nutrients typically derived from animal products such as vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids. However, with careful planning and supplementation if necessary, these challenges can be overcome.
It’s also important to remember the role of individual variation when adopting a plant-based diet. What works for one person may not work for another, and it’s crucial to listen to one’s own body and consult with a healthcare professional when making significant dietary changes.
The Future of Plant-Based Diets
The popularity of plant-based diets shows no signs of waning, with increasing numbers of people recognizing their potential benefits for health and the environment. As our understanding of nutrition evolves, the emphasis is likely to continue shifting towards more holistic, plant-centered dietary patterns.
However, the future of plant-based diets also relies on societal changes. Accessibility to healthy plant-based foods, education on proper nutrition, and supportive policies are all crucial to encourage more people to adopt plant-based diets.
In conclusion, plant-based diets, when well-planned and balanced, can provide a plethora of nutritional benefits and play a significant role in disease prevention and management. As we move forward, it’s essential to continue exploring and promoting the power of plants in our diets.